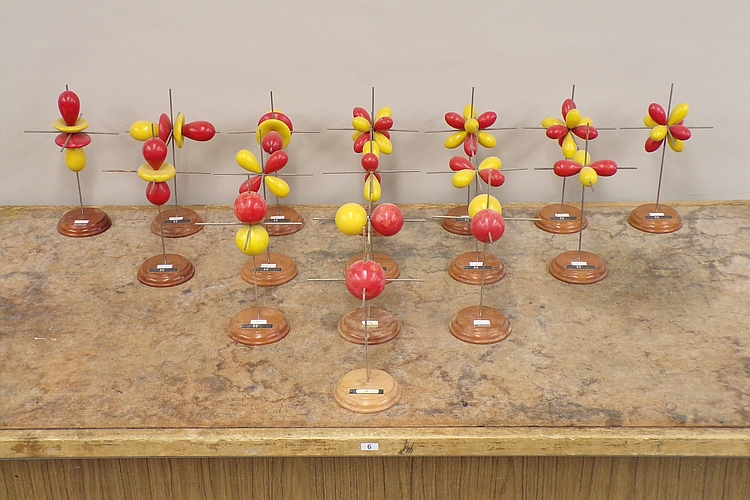
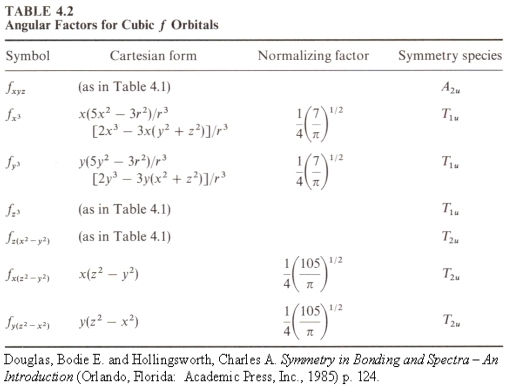
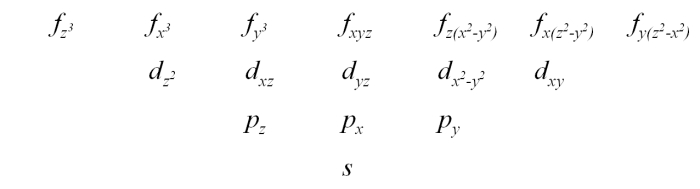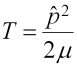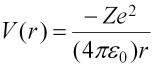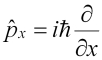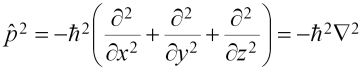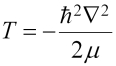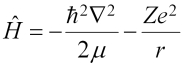The models in the photograph above represent the real parts of the angular portions of sixteen wavefunctions for an electron in a one-electron atom, that is, the angular portions of hydrogenlike wavefunctions, which are the eigenfunctions of the Schrödinger equation for an electron bound to a nucleus. Niels Bohr developed the first successful quantum theory of the hydrogen atom. He based this theory on the classical model of the electron traveling in circular orbits about the nucleus, but with the electron constrained only to certain allowed orbits. Arnold Sommerfeld then expanded Bohr’s model to yield sets of elliptical orbits. The squares of the functions depicted by the wooden models shown above would yield probability contours, that is, surfaces along which there is a particular (fixed) probability of finding the electron, and which enclose regions within which the total probability of finding the electron is a particular value, so it is not really proper to speak of the motion of the electron as an orbit. Because the Schrödinger equation does, in a sense, describe the motion of the electron, though, and because of the relationship between the new quantum theory and Bohr’s old quantum theory, we refer to these functions as “orbitals.” While some frown on the use of this word, its use is widespread, and in certain ab initio calculations, functions of a type proposed by John C. Slater form basis sets known as Slater-type orbitals (e.g., STO-3G is a basis set comprising Slater-type orbitals, each of which is obtained by combining three Gaussian functions). Below is an explanation of the hydrogenlike wavefunctions and the relationship between their forms and the particular sets of quantum numbers associated with them. First, however, a diagram showing the names of the orbitals depicted by the models above is in order. The orbitals they depict are, respectively:
A full development of the theory behind these orbitals, and its history, is beyond the scope of this web page, and the references that follow give excellent presentations of both. I will give here a brief overview of the Schrödinger equation, with some notes regarding the quantum numbers associated with the orbitals and their relation to the nomenclature and “shapes” of the orbitals.
The Schrödinger equation, in shorthand, is:
The operator on the left is the Hamiltonian, and the E on the right is the eigenvalue that gives the total energy. The Hamiltonian has two parts: T for the kinetic energy, and V for the potential energy, as follows:
.
, so , and
(the factor of 1/4πε0 has been omitted to make the simplification of using atomic units, which is why it was in parentheses) and the Schrödinger equation is:
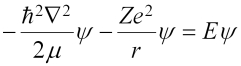
In all of the above, µ is the reduced mass of the system, or mM/(m+M), where m is the mass of the electron, and M is the mass of the nucleus (a proton for the hydrogen atom). The eigenfunctions take the general form:
The functions R are the radial distribution functions, Θ are the surface zonal harmonics, which cut a sphere along longitude lines, into segments like those of an orange, and Φ are the tesseral harmonics, which cut a sphere into tiles. The Θ and Φ parts together make up the spherical harmonics (also called surface harmonics), denoted by Ylm or Ylm, and the above may be written:
The indices n,l and m are three of the four quantum numbers that characterize the state of the electron. n, the principal quantum number, gives the energy level in which the electron resides, and can be any nonzero integer (1, 2, 3, . . .). Sometimes the energy levels are called shells, denoted by letter starting from k (k, l, m, . . .). l is the angular momentum, or azimuthal, quantum number, which is any integer, 0, 1, 2, . . . , n-1. m, which is often denoted by ml, is the magnetic quantum number, which ranges from -l, -l + 1, -l + 2, . . . , +l. The fourth quantum number is ms, for spin, which for an electron is ±1/2. An electronic orbital is denoted by n and a letter that stands for a given value of l. For l = 0, 1, 2, 3 the letters are, respectively, s, p, d, f, and for higher l, the letters that follow f in alphabetical order. The letters s, p, d and f stand for sharp, principal, diffuse and fine, which refer to series of absorption lines in atomic spectra, from transitions whose final (upper) states are s, p, d and f orbitals, respectively, or emission lines from transitions whose initial (upper) states are s, p, d and f orbitals, respectively. While these labels have only historical significance, they remain in use.
Given the constraints on l and ml, for n = 1, there is only one orbital, the 1s orbital. The next level, n = 2, has four orbitals: 2s, 2p-1, 2p0 and 2p1. For n = 3, we have one 3s, three 3p orbitals and five 3d orbitals, and for n = 4, there are one 4s, three 4p, five 4d and seven 4f orbitals. For n = 5 we add to the s, p, d and f orbitals nine 5g orbitals, and so forth. l gives the magnitude of the orbital angular momentum, and ml gives the magnitude of its component along the z-axis. We need not concern ourselves with ms. We can note, however, that the Pauli exclusion principle states that no two electrons can occupy the same state. In other words, no electron can have all four quantum numbers the same as those for another electron. Since ms has two possible values for an electron, this means that up to two electrons can occupy any atomic orbital as long as their spins are opposite.
The spherical harmonics are eigenfunctions of L2 and Lz, and are given by:
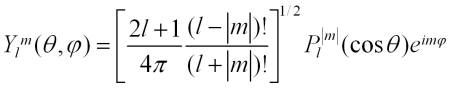
The Pl|m|(cos θ) are associated Legendre functions, Pl|m|(x), where x = cos θ. These functions are:
,
and they are obtained from the Legendre polynomials, which are:
,
so that:
,
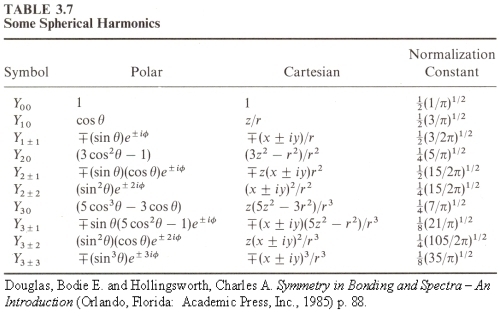
You can, of course, obtain the Θ part alone. Its normalization factor differs from that of the spherical harmonics by a factor of (1/2π)1/2, and it does not have the eimφ term. Below is a table showing some spherical harmonics.
Finally, we come to the shapes of the surfaces described by these functions. We can get an idea of these shapes by examining the set of quantum numbers, n, l and ml. We have up to now ignored the radial part of the wavefunction, but it is useful now to consider one of its basic features. The wavefunctions, as we can see by the varied shapes of the orbital models, may have a variety of nodes – places where the wavefunction changes sign. The radial part of the wavefunction has n - l - 1 nodes. These are nodes that occur as one goes outward from the nucleus along a radius, and are thus called radial nodes. They yield nodal spheres where they occur. Going around the atom at a fixed distance from the nucleus, one finds other nodes, called angular nodes, which can be either planes or cones. The number of angular nodes equals l. So the total number of nodes for a given orbital is n - 1. For example, a 1s orbital, for which n = 1 and l = 0, has zero nodes, and is spherically symmetric. A 2s orbital has n = 2 and l = 0, and so has one (radial) node. Roughly speaking, it resembles a sphere within a spherical shell. A 2p orbital has n = 2 and l = 1, and so has no radial nodes (2 - 1 - 1 = 0), but one angular node, which is the nodal plane that separates the two lobes of the orbital. (The pairs of tangent spheres in the models are only an approximation, and should really be pairs of distorted ellipsoids.) Similarly, a 3s orbital has two spherical nodes, a 3p orbital has one spherical node and one planar node, and a 3d orbital has either two conical nodes or two planar nodes, depending on ml and how the orbital is represented (vide infra). The pattern continues for the f orbitals, as you can see from the models in the photograph. In the models for the 3dz2 and the 4fz3, 4fx3 and 4fy3 orbitals, the central doughnut-like lobes should be separated from the other lobes by nodal surfaces. That is, each one should have a hole in the center. If we imagine including the radial functions as well, then as we increased n above 1, 2, 3 or 4 for the s, p, d and f orbitals, respectively, spherical nodes would appear, splitting the various lobes on each of the models.
Below is a table showing the angular portions of the wave functions for all the hydrogenlike orbitals up to 4f:
You will notice that the labels for most of the f orbitals differ from those listed for the models. The next table gives the angular portions of the 4f orbitals in the form that corresponds to the labels given for the models, which is that of the cubic set of f orbitals. These are obtained from orthogonal combinations of the functions in the table above (Table 4.1) such that the resulting orbitals are bases for representations of the point group Oh (that is, having octahedral symmetry).
It is also possible to obtain sets of equivalent orbitals in which all five d orbitals have the same shape (Powell, R.E., J. Chem. Ed., 45, 45 (1968), Pauling, L. and McClure, V. J. Chem. Ed., 47, 15 (1970)) and all seven f orbitals have the same shape (Schmelzer, A. Int. J. Quantum Chem., 11, 561 (1977); the papers by Pauling and McClure and by Schmelzer are cited in Douglas, Bodie E. and Hollingsworth, Charles A. Symmetry in Bonding and Spectra, where the tabes above come from). In fact, if you search on the web for graphical representations of these orbitals, some of the references you find will show such equivalent orbitals.
Below is a list of references that contain material on this subject:
1. Pauling, Linus and Wilson, E. Bright, Jr. Introduction to Quantum Mechanics With Applications to Chemistry (New York: The McGraw-Hill Book Company, 1935, reprinted by Dover Publications, Inc.). The classic! This book gives a thorough treatment of both the history and the mathematics.
2. Eyring, Henry; Walter, John and Kimball, George E. Quantum Chemistry (New York: John Wiley and Sons, Inc., 1944) Another classic. This book also gives a thorough treatment of the history and mathematics.
3. Herzberg, Gerhard. Atomic Spectra and Atomic Structure (New York: Dover Publications, 1944). Somewhat condensed treatment, but excellent overview.
4. Levine, Ira N. Quantum Chemistry, third edition (Newton, Massachusetts: Allyn and Bacon, Inc. 1983). Somewhat condensed history, full and beautiful mathematical treatment.
5. Karplus, Martin and Porter, Richard N. Atoms and Molecules: An Introduction for Students of Physical Chemistry (Menlo Park, California: W. A. Benjamin, Inc., 1970). Beautiful, comprehensive treatment, but does not cover Sommerfeld orbits.
6. Eisberg, Robert and Resnick, Robert. Quantum Physics of Atoms, Molecules, Solids, Nuclei and Particles (New York: John Wiley and Sons, Inc., 1974). Beautiful, full and comprehensive treatment of both the history and mathematics by a UCSB professor emeritus (Robert Eisberg)!Almost any textbook on general chemistry will also contain a simplified presentation of this material. Two excellent ones, which I consulted for writing this page, are:
1. Mahan, Bruce H. University Chemistry, third edition (Reading, Massachusetts: Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, 1975)
2. Zumdahl, Steven S. Chemical Principles, third edition (Boston: Houghton Mifflin Company, 1998)