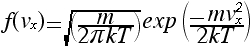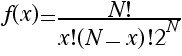
Since factorials become very large very fast, this formula is difficult to use even with a computer. In this problem we will try to find a better (even if it is an approximation) formula to use.
a) Use Stirling's approximation
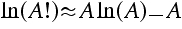 to show that f(x) can be approximated by:
to show that f(x) can be approximated by: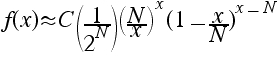
If Stirling's approximation has an error ε, what is the value of C in terms of ε?
This function is more computationally friendly than the original, but we can do even better...
b) It can be shown (with great difficulty) that our original f(x)--the one with the factorials--can be approximated for large N by a Gaussian:
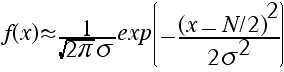
Assuming this can be done, let's estimate the standard deviation σ.
First calculate the ratio f(N/2 + 1) / f(N/2) for both functions. Then use the fact that
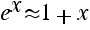 for x << 1 to estimate σ in terms on N.
for x << 1 to estimate σ in terms on N. 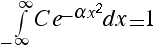
This integral can not be solved in closed form, i.e. there is no function whose derivative is a Gaussian. Luckily, there is a trick we can use to evaluate the integral.
a) Start by defining I such that
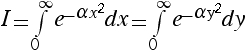 . We will not try to evaluate I, instead we will
try to find I2. Express I2 as an integral
of a function over the entire first quadrant of the xy-plane.
. We will not try to evaluate I, instead we will
try to find I2. Express I2 as an integral
of a function over the entire first quadrant of the xy-plane.b) Re-write this integral in polar coordinates.
c) Perform the integral using u-substitution. What is the value of I?
d) Using your result, find C in terms of α .
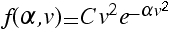 .
.a) Show that
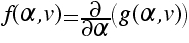 . What is g(α
,v)?
. What is g(α
,v)?b) Using your result from part a) and #2, find C in terms of α .