
X-Ray Diffraction
X-ray is very useful in many applications like the medical purpose and security
scanning. X-ray is also commonly used in physics like for determining crystal
structure. Since the characteristic wavelength of the x-ray is in the range
of an angstrom close to the size of unit cell of crystals, x-ray can then be
used to determine their structures by using Bragg scattering condition.
Our Experiment
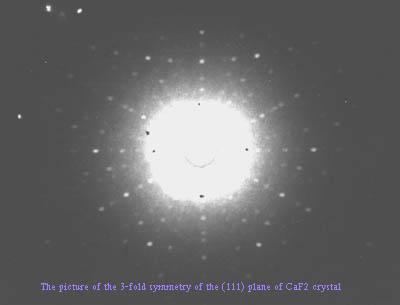
In our experiment, we use x-ray diffraction to determine a structure of a CaF2 crystal; Bragg-scattering angles at which laser beam reflected from the crystals constructively interfere will reveal the structure of the crystal. We will use two methods in this experiment. The Laue' method is used to determine the orientations of a single crystal and to confirm the type of the single crystal. The Powder method is used to determine the lattice spacing of the crystal.
With the Laue' method, we obtain the pictures of symmetries which confirm the FCC type of the CaF2 and the orientation of the crystal can be determined by the Greninger net. With the Powder method, the lattice spacing of the CaF2 crystal is determined to be 5.5 +/- 0.14 Angstroms.
Here are a few images by using the Laue' method:

Links to the websites about x-ray diffraction
A Non-Mathematical Introduction to X-ray Diffraction
High Resolution X-ray Diffraction
Growing Crystals That Will Make Your Crystallographer Happy
X-Ray Diffraction introduced by Squier Group at UC. San Diego
Teaching guide X-Ray and neutron diffraction
X-Ray Analysis of a Solid by Powder Method